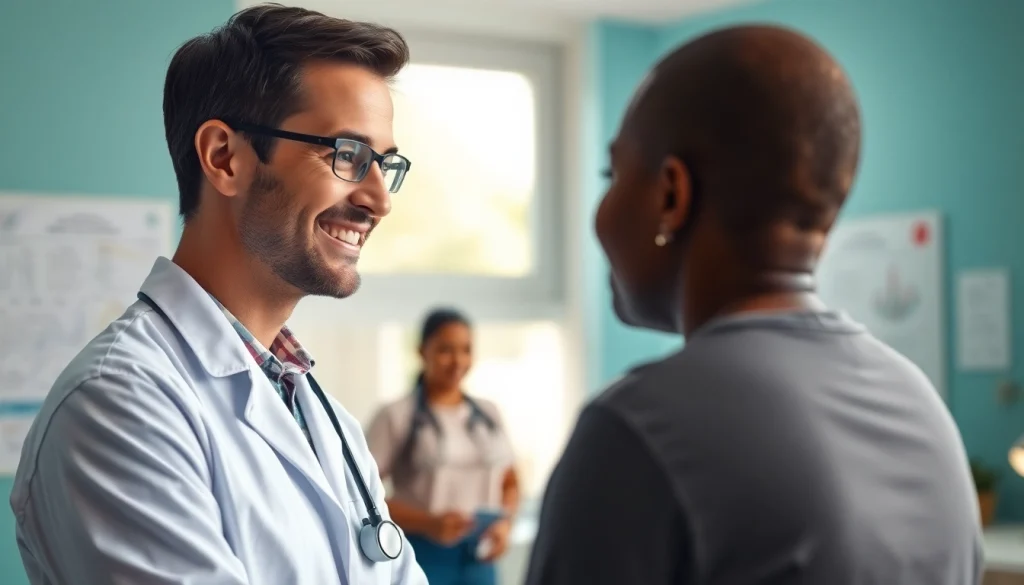
Understanding Health: Definition and Importance
Health is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various dimensions of well-being—physical, mental, and social. Understanding what health truly means is crucial for individuals, communities, and societies at large. It goes beyond the absence of disease, incorporating a holistic approach to well-being that includes living a fulfilling life. To explore this concept further, we must delve into its definition, differentiate between health and wellness, and recognize the immense benefits of prioritizing health in our daily lives. Engaging with topics such as Health is essential to promote overall well-being.
The Concept of Health
At its core, health can be defined as a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being. This definition, provided by the World Health Organization (WHO), moves beyond mere absence of illness, recognizing a broader dimension that includes emotional and social connectivity. It implies a dynamic state where individuals can lead fulfilling lives, adapted to their environment while effectively managing stressors and the variations of life circumstances. Moreover, health is influenced by various factors such as genetics, environment, lifestyle choices, and economic conditions.
Health vs. Wellness: Key Differences
Often, the terms “health” and “wellness” are used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts. Health refers to the current state of a person’s physical, mental, and social well-being, while wellness is an active process of becoming aware of and making choices toward a healthy and fulfilling life. Wellness emphasizes a proactive approach; it is about enhancing well-being through lifestyle choices, emotional resilience, and social connectedness. Recognizing these differences enables individuals to take a more informed approach to improve both their health and overall wellness.
Benefits of Prioritizing Health
Prioritizing health brings about numerous benefits that affect not only individuals but also communities and economies. Healthy individuals are more productive, engaging fully in their work and contributing to their communities. They experience lower rates of chronic diseases, which in turn reduces healthcare costs. Moreover, good health fosters a positive mindset, enhancing emotions such as happiness and satisfaction. It also cultivates strong relationships, as individuals in good health tend to engage more socially, thereby strengthening the social fabric of communities.
Key Components of Health: Physical, Mental, and Social
A comprehensive understanding of health requires an examination of its key components—physical, mental, and social health. Each component plays a vital role in shaping overall well-being and requires attention and care.
Physical Health: Foundations and Practices
Physical health is often the most recognized aspect of health and pertains to the efficient functioning of the body. Maintaining physical health involves regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate rest, and preventative healthcare measures. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity weekly is recommended for adults, coupled with muscle-strengthening exercises twice a week. Nutrition also plays a crucial role; a diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for optimal function and vitality.
Mental Health: Significance and Support
Mental health is equally vital, encompassing emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects cognition, perception, and behavior. Mental health issues can arise from various sources, including stress, trauma, and biological factors. Recognizing the signs of mental health challenges—such as persistent sadness, anxiety, or changes in mood—is crucial. Support mechanisms such as therapy, counseling, and mindfulness practices can significantly enhance mental resilience. Engaging in activities that promote mental clarity, such as meditation, journaling, or simply spending time in nature, can also be beneficial.
Social Health: Building Strong Relationships
Social health reflects how individuals interact with others and their capacity to form meaningful connections. Good social health contributes to overall well-being, providing a support system and a sense of belonging. Building and maintaining relationships requires effort, communication, and emotional intelligence. Participation in community activities, support groups, and social networks can enhance social health. It is also essential to recognize and nurture important relationships, ensuring that connections foster positivity and emotional support.
Common Health Challenges and Solutions
Despite our best efforts, various health challenges can impede well-being. Acknowledging these challenges and proactively addressing them is vital for maintaining health.
Chronic Diseases and Prevention Strategies
Chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity are significant health challenges that require dedicated prevention strategies. Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in preventing these conditions. Regular health screenings, maintaining a balanced diet, and engaging in consistent physical activity are foundational strategies to mitigate risks. Education on the impacts of smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor dietary choices can empower individuals to make healthier decisions. Initiatives that promote understanding about these diseases can play a pivotal role in community prevention efforts.
Mental Health Issues: Signs and Interventions
Mental health issues may manifest in various forms, from anxiety and depression to more severe conditions such as bipolar disorder or schizophrenia. Awareness of the signs of mental health issues is essential for early intervention. Changes in appetite, sleep disturbances, withdrawal from social activities, and persistent feelings of hopelessness are critical indicators. Access to mental health resources, such as therapy and support groups, can provide the necessary interventions. Normalizing conversations about mental health can also encourage individuals to seek help without stigma.
Addressing Lifestyle-Related Health Problems
Lifestyle-related issues such as obesity, heart disease, and stress-related conditions are increasingly prevalent. Addressing these issues requires an integrated approach that combines education, community support, and policy changes. Workshops that promote cooking skills, nutrition education, and fitness activities can empower individuals to make healthier lifestyle choices. Additionally, promoting mental well-being through stress management initiatives can alleviate lifestyle-related health issues. Community resources, including fitness groups and wellness programs, can facilitate lifestyle changes that lead to better health outcomes.
Practices That Promote Health
Engaging in health-promoting practices is essential for enhancing overall well-being. These practices reinforce the importance of self-care and proactive health management.
Nutrition: Eating for Optimal Health
Nutrition is the foundation of health. A nutrient-dense diet is vital for providing the body with the necessary vitamins and minerals to function optimally. Emphasizing whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential. Meal planning, cooking at home, and learning about portion control can support healthier eating habits. Moreover, understanding food labels and making informed choices when dining out can empower individuals to take control of their nutrition.
Exercise: Importance and Recommendations
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of health, contributing to physical fitness, weight management, and mental well-being. Engaging in a mix of aerobic and strength training exercises can enhance cardiovascular health and muscle mass. It is vital to find activities that are enjoyable, whether it’s hiking, swimming, dancing, or team sports; this ensures consistency and longevity in exercise habits. Setting realistic goals and progressively increasing activity levels can also help maintain motivation. Importantly, integrating movement into daily routines, like walking or cycling instead of using a car, can enhance overall activity levels.
Mindfulness and Health: Practices for Mental Clarity
Mindfulness practices can significantly enhance mental clarity and emotional resilience. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can reduce stress and improve concentration. Regular mindfulness practices encourage individuals to live in the moment, enhancing the appreciation of life’s small joys. Incorporating mindfulness into daily routines can promote emotional stability and decrease anxiety. Furthermore, mindfulness encourages a balanced perspective on health, promoting sustainable lifestyle changes rather than quick fixes.
Evaluating Health: Metrics and Measurements
Measuring and evaluating health is crucial for understanding the impact of lifestyle choices and interventions. Specific metrics can guide individuals toward healthier behaviors.
Key Health Indicators to Monitor
Monitoring key health indicators such as Body Mass Index (BMI), blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels can provide insights into personal health. Regular check-ups are essential to keep track of these metrics and identify potential health challenges before they escalate. Engaging healthcare professionals in these evaluations ensures that individuals receive accurate information and guidance tailored to their health needs.
The Role of Health Screenings and Checkups
Regular health screenings and checkups can play a pivotal role in preventive care. They provide opportunities for early detection and management of chronic diseases. Various screenings may include mammograms, colonoscopies, and diabetes tests, depending on individual risk factors and guidelines. Staying informed about recommended screening schedules can facilitate proactive health management, allowing individuals to take control of their health outcomes.
Using Data to Enhance Health Outcomes
Data collection and analysis are fundamental in enhancing health outcomes. Tracking personal health metrics through wearables, health apps, or journals can provide valuable insights into patterns and triggers related to health. Additionally, larger health datasets can inform public health policies and community resource allocation. By leveraging data analytics, individuals and health organizations can create targeted interventions that meet specific health needs.