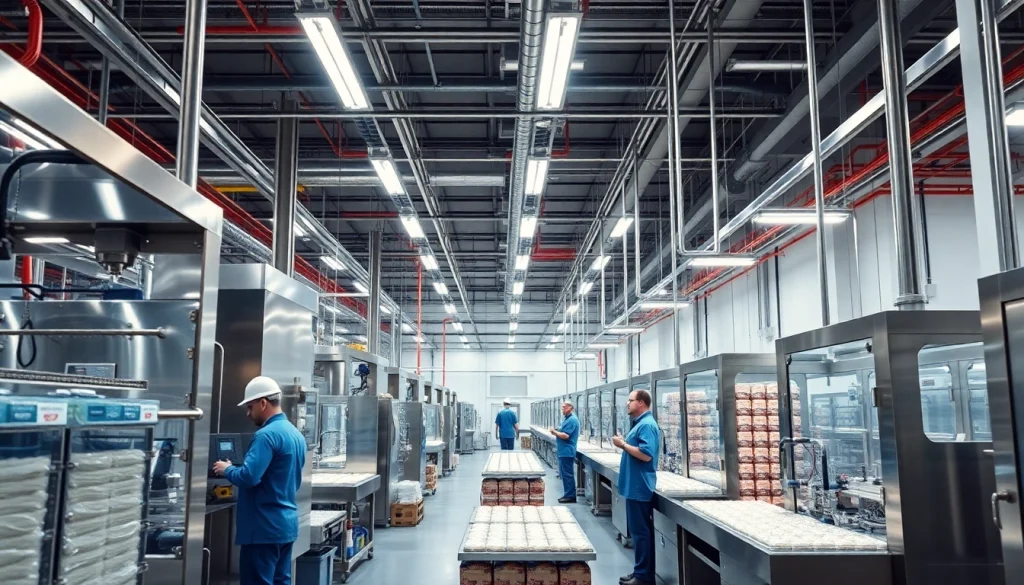
The Basics of a Sweetener Factory
In the modern food industry, sweeteners play a vital role, enhancing taste while also impacting health and nutrition profiles. A sweetener factory is integral to this ecosystem, utilizing advanced processes to produce a variety of sweetening agents. Understanding the inner workings of such a facility is crucial for manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers alike.
Key Components of Sweetener Production
Sweetener production is complex and involves several key components:
- Raw Materials: Depending on the type of sweetener, raw materials may include sugars, natural extracts, or artificial compounds. The sourcing quality heavily affects the final product.
- Production Machinery: Specialized equipment is necessary for processes like extraction, purification, and crystallization. These machines must adhere to stringent hygiene and efficiency standards.
- Quality Control: Continuous monitoring helps ensure that the sweeteners meet required specifications and safety standards. This includes sampling, testing, and auditing protocols.
Types of Sweeteners Produced
Within a sweetener factory, various sweetening products can be manufactured:
- Naturally Derived Sweeteners: Sweeteners like honey, agave, and stevia fall into this category, offering a more wholesome alternative to refined sugars.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Products such as aspartame and sucralose belong here, providing intense sweetness with fewer calories.
- Blended Sweeteners: Combination sweeteners aim to balance taste and calorie counts, mixing natural and artificial inputs to achieve desired flavors.
Overview of Factory Operations
The operations within a sweetener factory are methodical and structured. They can be broken down into distinct phases:
- Raw Material Processing: The journey begins with the processing of raw materials, where they are cleaned and prepared for further steps.
- Extraction and Refinement: Sweetening agents are extracted from raw sources, followed by purification to eliminate impurities and maximize quality.
- Product Formulation: Tailoring sweeteners to meet market needs involves blending ingredients and adjusting sugar levels to create product variants.
- Packaging and Distribution: Final products are packaged for distribution, often emphasizing sustainability in packaging choices.
Technological Innovations in Sweetener Factory
Technological advancements continually reshape the operation of sweetener factories, enhancing both efficiency and safety.
Automation in Manufacturing
Automation is increasingly prevalent in sweetener production. By incorporating robotics and AI, factories can:
- Minimize human error, ensuring consistent quality.
- Optimize production speeds, reducing turnaround times.
- Implement predictive maintenance, decreasing downtime.
Quality Control Measures
Modern sweetener factories invest significantly in technology for quality control:
- Real-time Monitoring: Utilizing sensors and data analytics, plants can monitor various parameters continuously, ensuring product consistency.
- Automated Lab Testing: Automation in laboratories reduces testing time while increasing accuracy in quality assessment.
- Traceability Systems: Advanced tracking systems ensure that each batch can be traced back to its raw materials, enhancing transparency.
Environmental Considerations
As sustainability becomes a priority, sweetener factories are adapting their processes to minimize environmental impacts:
- Waste Reduction: Innovative techniques reduce waste generation during production, focusing on recycling and repurposing by-products.
- Energy Efficiency: Factories are incorporating energy-efficient machinery and practices to reduce their carbon footprints.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Many sweetener factories are shifting towards sustainably sourced raw materials, ensuring environmentally friendly production.
Choosing a Sweetener Factory: What to Look For
Selecting the right sweetener factory can impact your business’s success. Here are essential factors to consider:
Understanding Product Range
It is crucial to comprehend the variety of sweeteners a factory offers. A wider product range means better flexibility to meet diverse market demands. Ensure that products comply with varying dietary preferences, such as organic or low-calorie options.
Evaluating Supply Chain Efficiency
A reliable supply chain is vital for uninterrupted production. Evaluate the factory’s logistics, including raw material acquisition and distribution strategies, to ensure timely deliveries and minimal disruptions.
Assessing Customer Support and Service
Quality customer service can set a factory apart. Look for providers that offer comprehensive support, including technical assistance, product development consultations, and responsive communication channels.
Common Challenges in Sweetener Factory Operations
Every sweetener factory faces challenges that can impact production. Identifying and addressing these issues is key to operational success.
Addressing Supply Chain Disruptions
Unforeseen disruptions, such as raw material shortages or transportation delays, can significantly hinder production timelines. Implementing dual sourcing strategies and maintaining inventory buffers helps mitigate these risks.
Maintaining Quality Standards
Consistency in quality is paramount for customer satisfaction. Factories should adopt stringent inspection processes and regularly train staff to maintain product quality.
Compliance with Regulations
Adherence to food safety and labeling regulations is a must. Factories must stay updated on relevant regulations and ensure that their production processes comply to avoid potential penalties.
The Future of Sweetener Factories
As the landscape of sweetener production evolves, several trends are likely to shape the future of sweetener factories:
Emerging Trends in Sweetener Production
Several trends are emerging in sweetener production, including greater demand for plant-based options and innovations like fermentation-derived sweeteners. These shifts are influenced by consumer preferences for healthier and more sustainable products.
Consumer Preferences Shaping Manufacturing
With growing health consciousness, consumers increasingly prefer products with natural sweeteners. Factories may need to adapt by diversifying their product lines to accommodate these changing preferences.
Investments in Sustainable Practices
Future sweetener factories will likely focus on sustainability. Investing in eco-friendly processes, from sourcing to distribution, will become a hallmark of successful operations, meeting both customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of sweeteners can be produced in a sweetener factory?
A sweetener factory can produce various sweeteners, including natural sweeteners like stevia, artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, and blended sweeteners combining different sources.
How does automation benefit sweetener production?
Automation enhances efficiency by reducing human error, optimizing production speeds, and implementing predictive maintenance, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved product quality.
What are the environmental considerations for sweetener factories?
Sweetener factories are focusing on waste reduction, energy efficiency, and sustainable sourcing to minimize their environmental impact and adhere to growing sustainability standards.
How can supply chain issues affect sweetener production?
Supply chain disruptions, like raw material shortages or delayed transportation, can halt production. Factories can mitigate risks by having dual suppliers and inventory buffers.
What role does quality control play in a sweetener factory?
Quality control ensures that products meet safety and quality standards. Continuous monitoring, automated testing, and rigorous auditing help maintain product consistency.